OSS Questionnaire
1. Background
As a continuation of the tradition since the release of the China Open Source Community Survey 2015 in early 2016, at the end of 2023 we launched another annual participatory survey of Chinese open source communities, dedicated to presenting the overall state of open source development in China in a multi-dimensional manner through continued developer survey reports.Using tools such as data analysis and survey reports, we have succeeded in producing a map of China’s open-source world in 2023.
The questionnaire addresses the multiple roles of the interviewees and aims to gain insight into community development trends at various levels.Based on the level of participation of the open source community, the respondents are divided into several roles: users, participants, contributors, maintainers, and ecosystem operators.This shapes onion model and layer evolution.The four role levels are defined as:
- User:users who have used one or more open-source products
- Participant:Users who interact with the open source community (e.g. communication with open source communities, participation in activities of open source community organizations, etc.)
- Contributor: Users who contribute substantially to the open source community(including code and non-code contributions.)
- Maintainer:Users primarily responsible for daily operations to the open source community (including project maintainer, PCC members, etc.)
In addition, ecosystem operators are the users who are primarily responsible for day-to-day operations in the open source communities, at a level above the participants and collectively referred to as operators.In addition to raising basic questions for all interviewees, the questionnaire addresses several different roles for users, contributors and operators.
The basic information for this questionnaire is as follows:
- Audiences :covers developers, community members, contributors, students, government and enterprise mangagement personnel.
- Topics :mainly covers personal information, work status, open source communities, developer technologies, etc.
- Method :Collects samples and data using online questionnaires to analyze data across comparisons
- Channels :KAIYUANSHE, KubeCon + CloudNativeCon + Open Source Summit China, 2023 Eighth Annual Open Source Conference in China, 2023 Open Atomic Developers Conference, 2023 Open Source Industry Ecology Conference
- Question Type * :single-choice, multiple-choice, open-ended
- Number of Questions :43
- Sample Quantity :875
2. Preview of questionnaire results
Characteristics of Respondents
- The age distribution of the interviewees is evenly distributed, with general education above undergraduate level. Gender and regional distributions align with the geographical distribution of developers in China, covering various roles in the computer industry.
Open Source Participation
- The activity of the open source community is an area of particular concern for the interviewees;Artificial Intelligence has become a technical area of concern for the majority of the interviewees.
Open Source Contributions
- Interviewees contribute more to warehouses of Technical Base Type; respondents are more motivated by Communities / Honorary Motivations and require less material incentives.
Community Operations Survey
- Most of the operators interviewed are in the open source community**.Nearly half of the respondents' respective companies prioritize the standardization and management of open source software usage.
Household Open Source Development Survey
- The respondents are optimistic about the future development of open sources in the country.With regard to the evolution of artificial intelligence in open source ecology, developers generally appreciate the prospects for its application in increased efficiency, automated testing and data analysis and consider that data security, transparency, ethics are the main challenges.
3. Analysis of the Questionnaire
3.1 Features of the Interviewee
First, we conduct surveys from the point of view of age, gender, academic qualifications, resident city, industry and professional identity, through which basic information about participants can be obtained, thus analysing the identity of the audience groups in open source communities.
3.1.1 Age, Gender, Education, City
| Age | Gender |
|---|---|
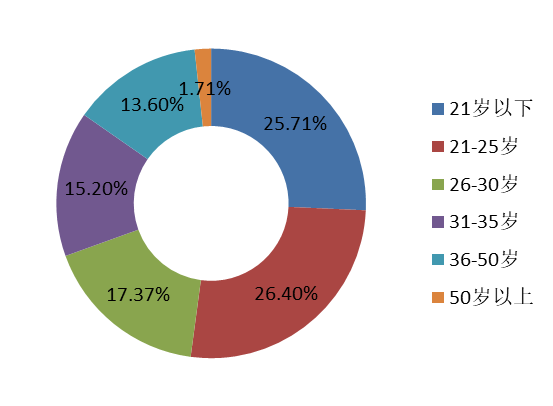 |  |
The age distribution of respondents to this questionnaire is similar to that of previous years, mainly in the 21-50 age group, with a more balanced age distribution.It is worth noting that the proportion of respondents under 21 years of age is 25.71%, a significant increase from 8.42% last year.The participation of young respondents in the table has increased considerably.
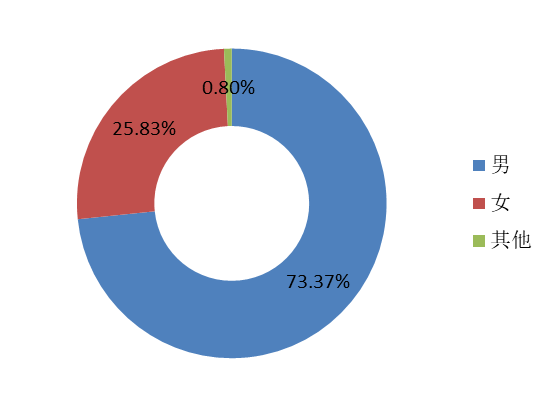
In terms of gender, male respiondents account for a higher proportion, reaching 73.37%, while females accout for 25.83%. Compared to last year's questionnaire, the proportion of women and men interviewed has increased significantly and is consistent with the current lack of gender balance among developers.
| Educational background | Region |
|---|---|
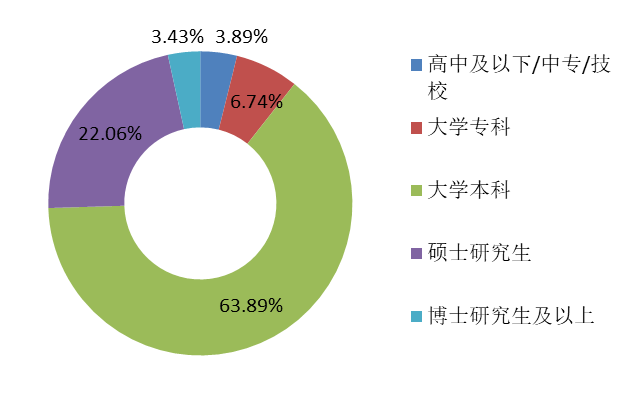 | 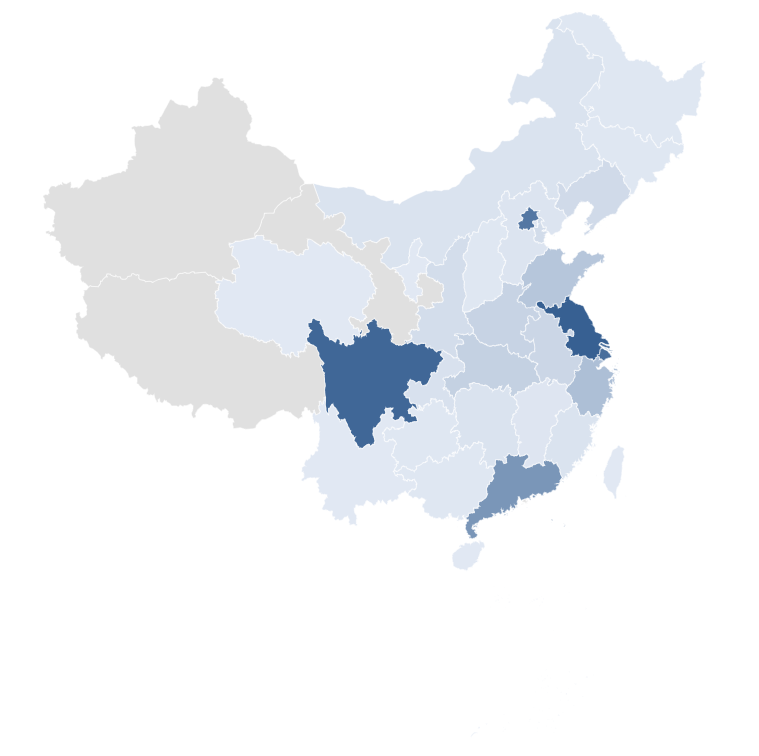 |
Respondents generaly have an educational background of at least a bachelor's degree; in urban distribution, the majority of the respondents are from Jiangsu, Sichuan and Shanghai, partly because our online sources of questionnaire collection are in those cities.There are also more interviewees in Beijing and Guangdong provinces, and there is a more consistent distribution of developers in the overall distribution and data sets.
3.1.2 Occupation in Industry, Profession
| Industry | Career status |
|---|---|
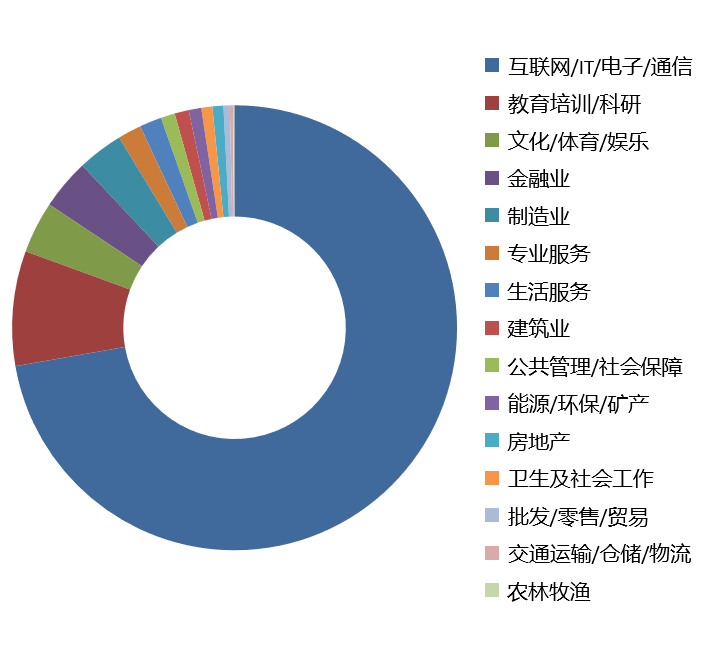 | 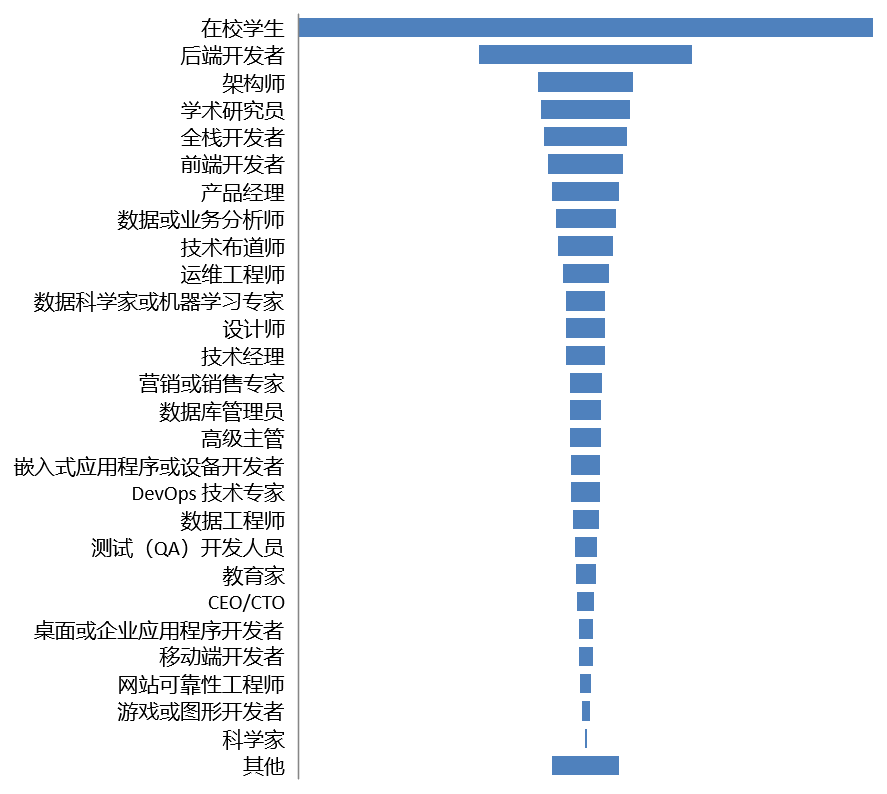 |
The majority of the respondents are in the Internet/IT / electronic/ communications industry, accounting for 72.23%, indicating that the survey primarily covers the field of science and technology.
In terms of professional status, 43.20% of students are in school, followed by back-end developers, architects and academic researchers. Overall, the respondents are predominantly technical practitioners and students and cover a number of occupations in computer industries.
3.2 Open source participation
3.2.1 Level of participation by open source communities
| Role of open source communities | Time to contact open source |
|---|---|
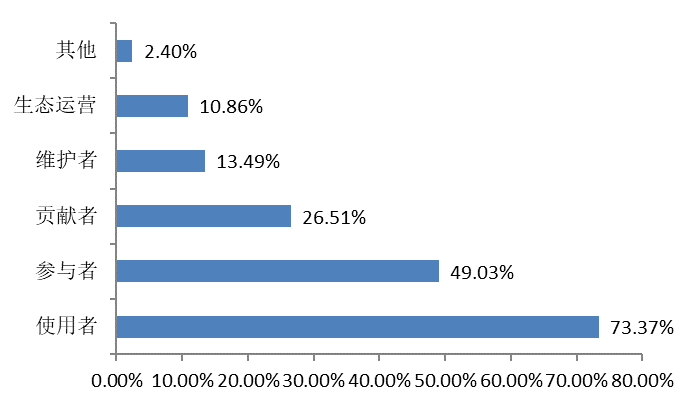 | 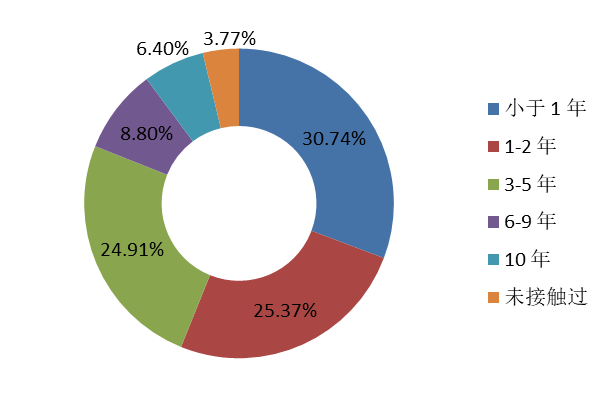 |
The survey shows that the vast majority of members of open source communities are users (73.37%), while close to half of the participants (49.03%) and some contributors (26.51%).
Regarding the duration of involvement in open source, one-third of respondents have been involved in open source communities for less than a year, while nearly half have more than 3 years of experience.
We have cross-analyze the question "To what extent do you think you are a member of an open source community" with interviewees' roles in an open source community.
| Extend of Considering Oneself a Part of the Open Source Community |
|---|
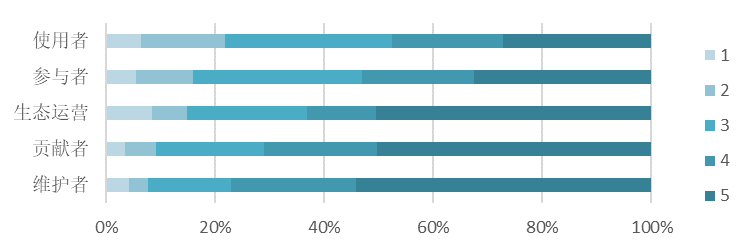 |
It can be seen that there is a greater sense of belonging among the maintainers, contributors, ecosystem operators than participants and users in the open source community.
The following questions were addressed to respondents who had a role in the open source community at the “user” level and above.
3.2.2 Use of Open Source Products
| Reason for Selecting Open Source Products | Factors Influencing Choice |
|---|---|
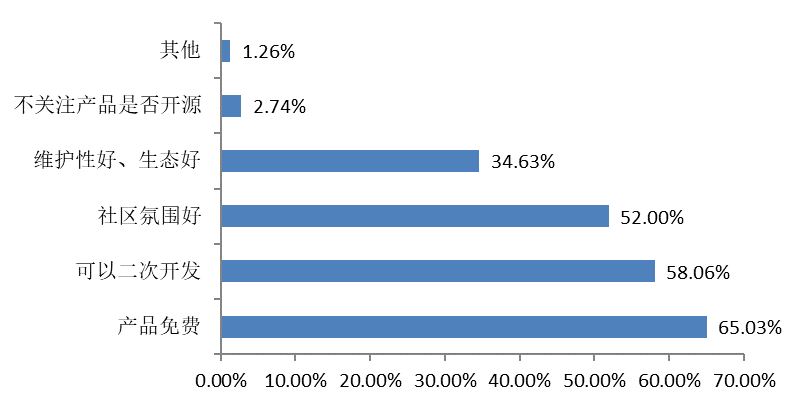 |  |
The main reason that users chose to use open source software is free of charge for their products, followed by further development and a favourable community environment.
In selecting open source products, participants are more focused on the level of code regulation and the activity of developers. This indicates that users are concerned not only about the functionality and quality of open source products, but also about the activity of communities and developers and the sustainability of projects.
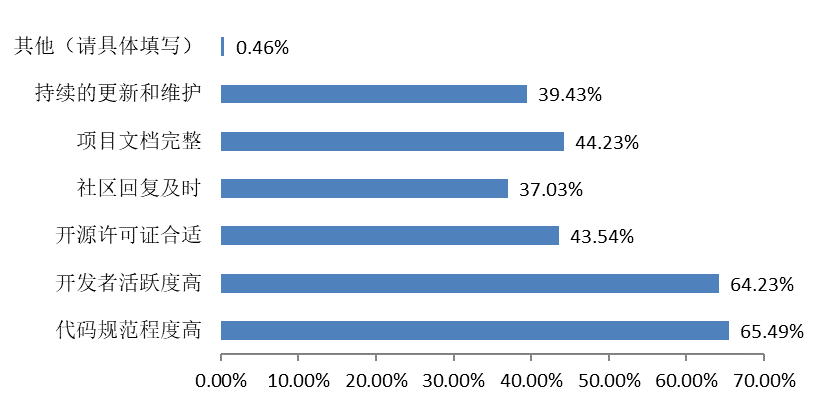
| Issues Encounterred When Using Open Source Products | Factors Prompting Open Source Contributions |
|---|---|
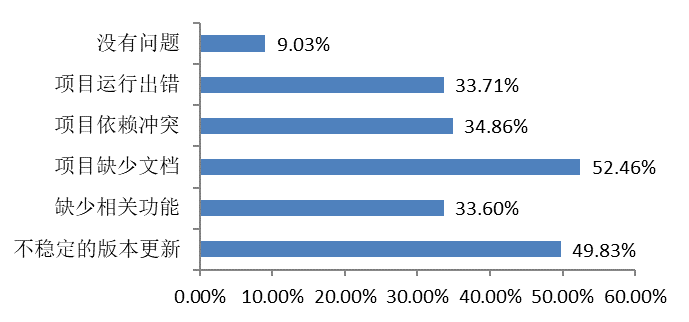 |  |
Among the problems encountered, the most common is the lack of documentation for the project, followed by an unstable update.
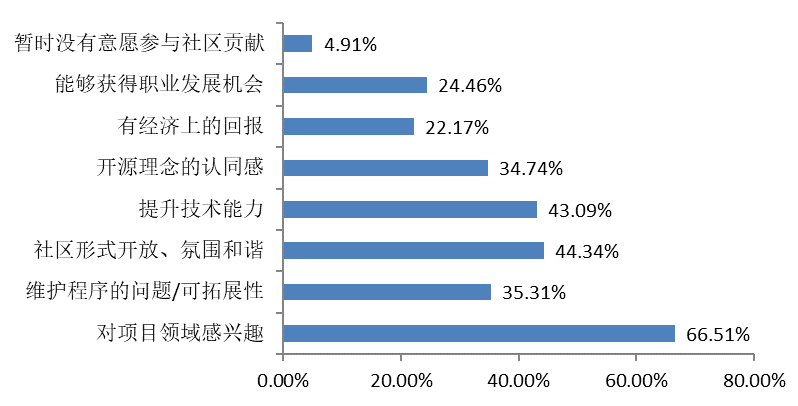
Factors such as personal interest, community atmosphere and technological upgrading play an important role in promoting open-source contributions.
3.2.3 Technical Direction
| Interested Technical Directions | Known Open Source License |
|---|---|
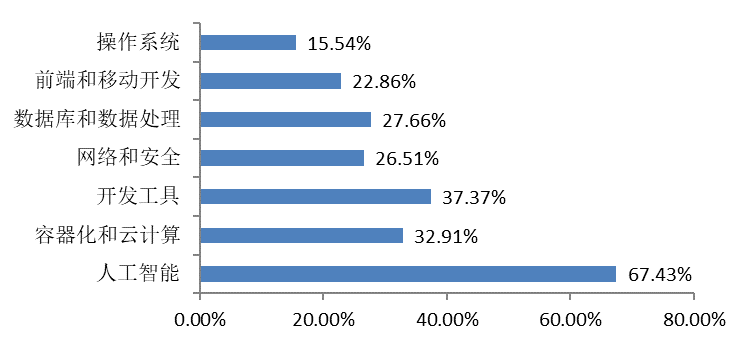 |  |
The interviewees show strong interest in artificial intelligence, accounting for 67.43%, followed by development tools, containerization and cloud computing.
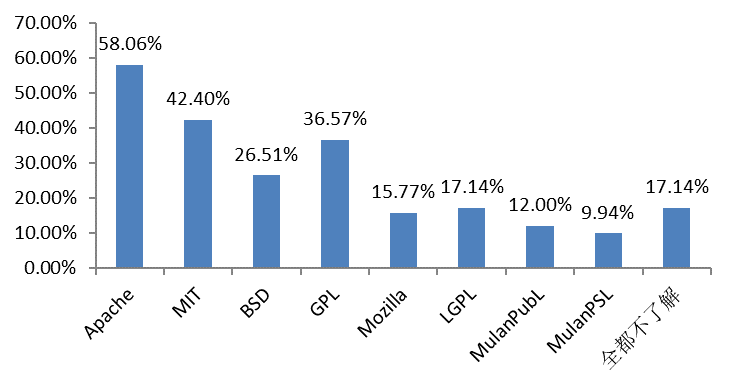
For open source licenses, Apache is the most popular option, followed by MIT and GPL.
3.2.4 Information Exchange
| Ways to Retrieve Open Source Products | Communication Methods with the Community |
|---|---|
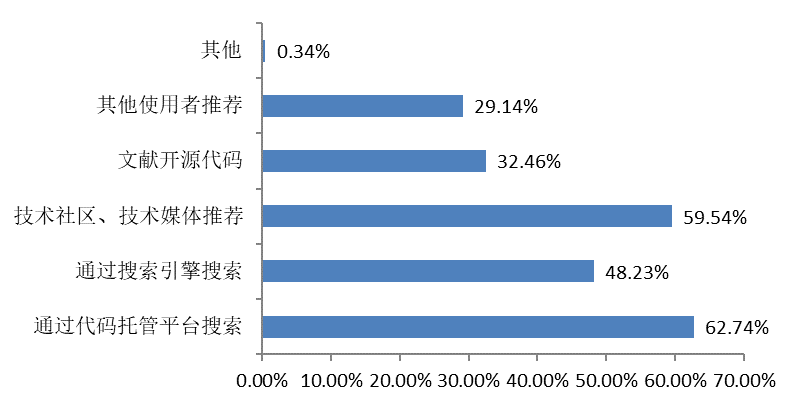 |  |
When searching for open source products, most people search through code-hosting platforms, technical communities or media recommendations, and search engines.
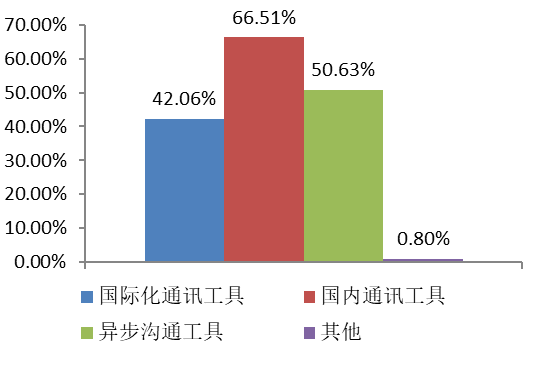
Communication with open source communities is mainly in the form of domestic communication tools (e.g. DingTalk, WeChat, QQ, Feishu, etc.) and asynchronous communication tools (e.g. GitHub Issue, Discussion, Mail List etc.), while internationalized communication tools (e.g. Slack, Skype, Telegram, Lark and others) are also widely used.The international open source community is characterized by a predominance of asynchronous communication tools, which differ remarkably from domestic practices.
| Frequently Used Products / Technology Community | Media to Get Open Source Information |
|---|---|
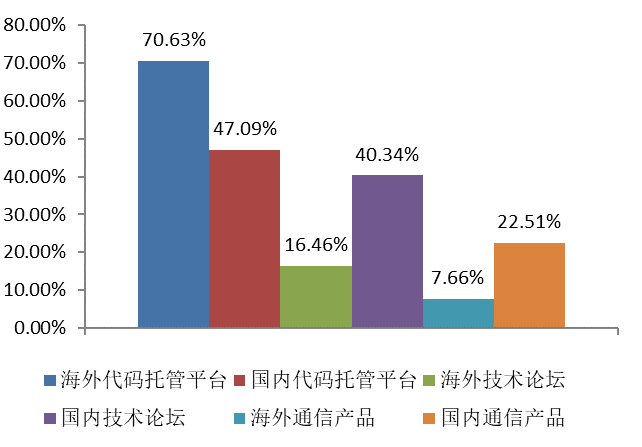 |  |
Interviewees are mainly engaged through a code hosting platform and open source community participation. In addition, a large number of respondents participate in open source communities through domestic technical forums.
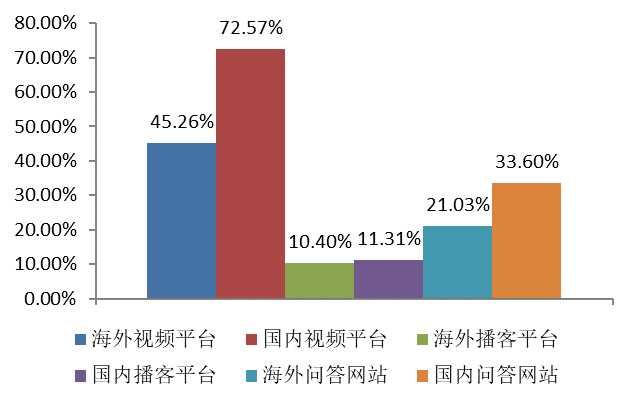
In terms of access to open source information, video platforms and question-and-answer websites are the main options, reflecting the preference of developers for access to open-source knowledge, including through audio-visual and interactive question-and-answer sessions.
3.3 Open Source Contribution
This section's questions are aimed at respondents whose roles in the open source community are "contributors" and above.
3.3.1 Level of Open Source Contribution Participation
| Participation in Open Source Project Activity | Time of Weekly Open Source Participation |
|---|---|
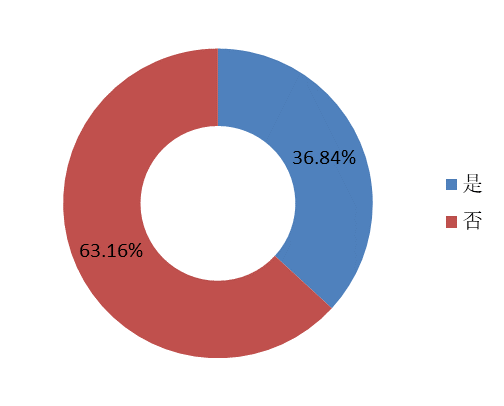 | 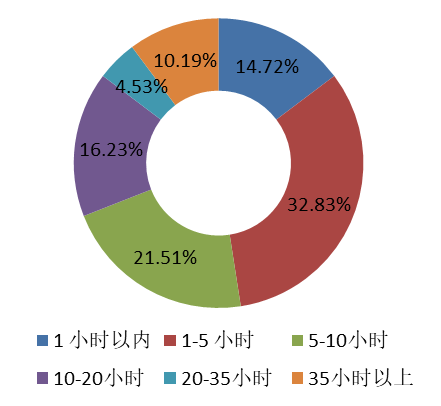 |
One third of student developers have been involved in open-source activities such as Google Summer (GSoC) and Open Source Lighting Scheme (OSPP); more than half of contributors have been involved in open source activities for more than 5 hours a week, and more than 10% of contributors have participated in open source activities for 35 hours a week, nearly reaching the standard of full-time developers.
3.3.2 Ways of Contributing to Open Source
| Main Open Source Contribution Platforms | Commonly Used Development Laungauges for Open Source Contributions |
|---|---|
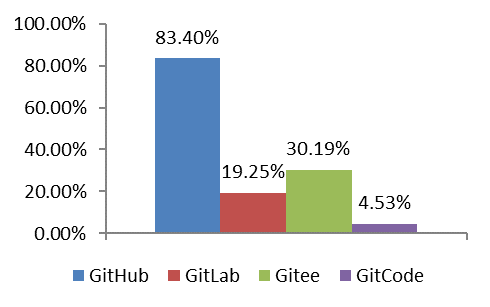 | 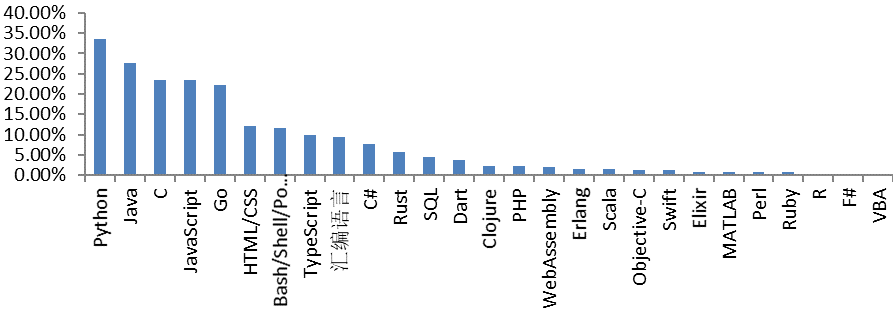 |
GitHub remains the preferred platform for the most respondents, occupying a dominant position, followed by Gitee and GitLab. This indicates that among Chinese developers, GitHub still holds significant influence, although domestic platforms are gradually emerging. The main development languages used include Python, Java, C, JavaScript, Go. In addition, HTML/CSS, TypeScript and others are given a high number of choices.
3.3.3 Open Source Contribution Content
| Main Types of Contributions | Types of Contributed Projects |
|---|---|
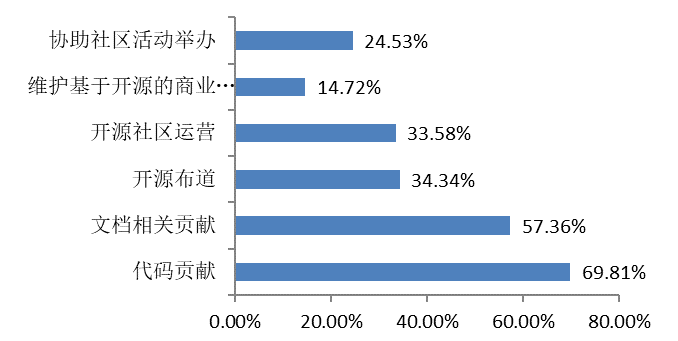 |  |
Interviewees contribute to open source projects mainly by writing codes and documents. In addition, open source advocacy, open source community operations and facilitating community activities are also common contribution methods.
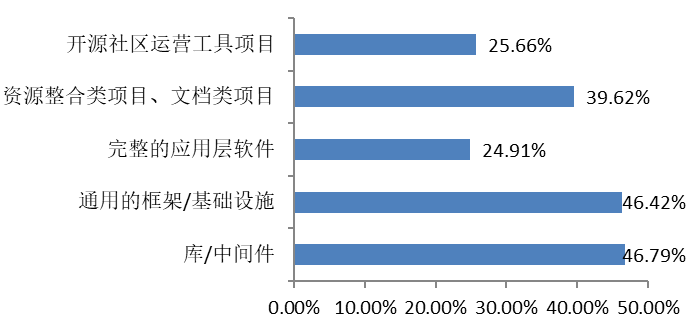
The types of open-source project that contributed are mainly concentrated in library/middleware and common framework/infrastructure, reflecting developers' deep interest in foundational technologies.
3.3.4 Incentives
| Incentives | Sources of Financial Return |
|---|---|
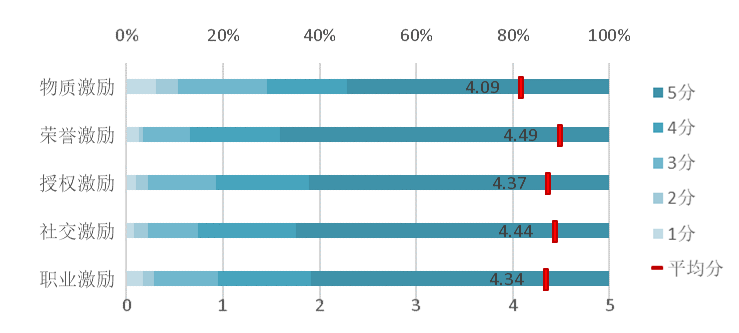 |  |
Various incentives have been positively evaluated, indicating that the diversity of incentives has had a positive impact on open source participation by developers. In particular, respondents believe that incentives for honour and social interaction have a more significant positive impact on contributions.
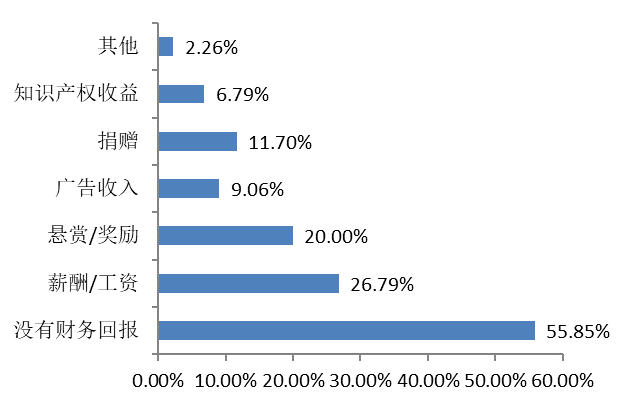
More than half of the developers participating in open source projects receive no financial rewards.The rest of the developers receive direct financial returns through compensation/salary, rewards/incentives, while very few developers receive financial support through advertising revenue, donations, and patent/intellectual property income.
3.4 Community Operations Survey
This section of the question is addressed to interviewees who are “operators” in the open-source community.
3.4.1 Overview of Open Source Communities
| Number of Community Users | Active Developers |
|---|---|
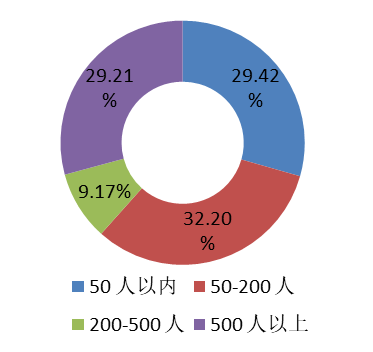 | 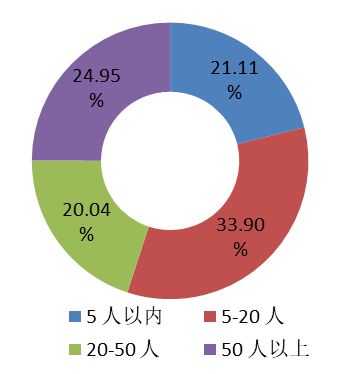 |
Nearly 60% of operators belong to open source communities with fewer than 200 users, while almost 30% belong to communities with over 500 users. More than half of the operators belong to the communities with fewer than 20 active developers.
3.4.2 Open Source Community Management
| Community Management | Community Commercial Support |
|---|---|
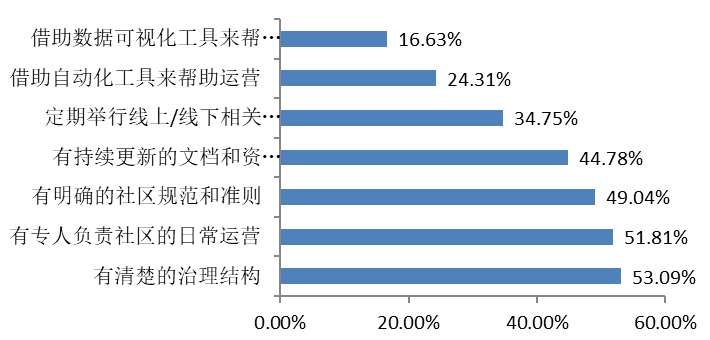 | 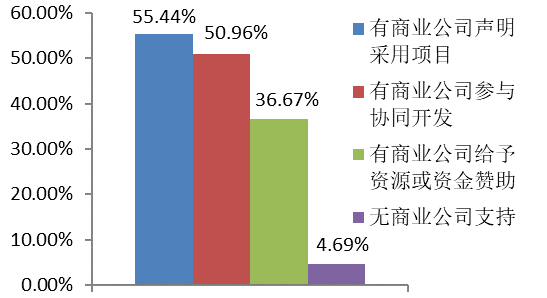 |
About half of the communities have clear governance structures and professionals responsible for day-to-day operations. At the same time, communities have generally developed clear norms and provided updated documentation to support member inclusion.
Most open source communities have commercial support and are mainly in the form of declarations and synergistic development.
3.4.3 Research on the Commercailization of Open Source Software
| Usage of Open Source Software in Enterprise | Agreement with commercialization of Open Source Projects |
|---|---|
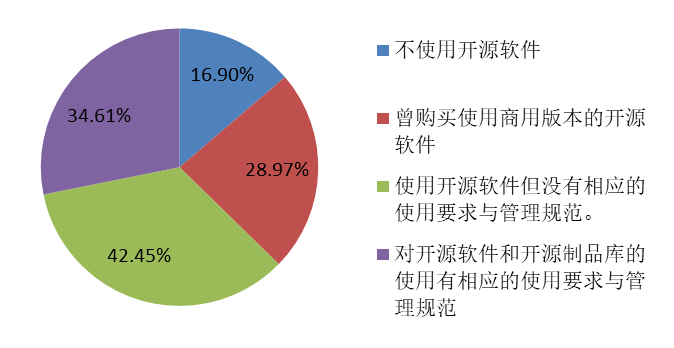 |  |
The vast majority of businesses use open-source software, with a clear ratio of 5:6 between samples with clear usage requirements and regulatory norms and those lacking corresponding management standards. This indicates that while some companies emphasize standards and management when using open source software, a large proportion of enterprises are still more loosely regulated, which may be influenced by factors such as company size, industry differences, and understanding of open source software.
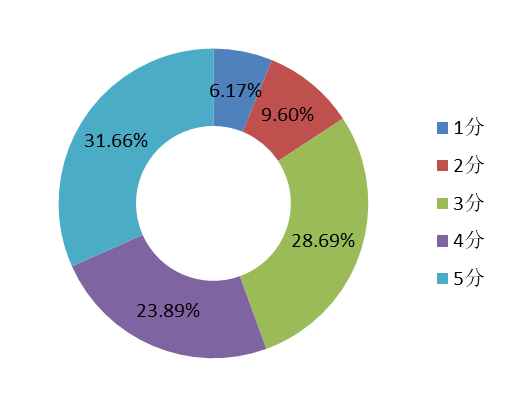
The level of acceptance for the use of open source projects for commercialization averages 3.65, with 31.66% gaving the highest acceptance ratings, indicating that most respondents hold a moderate to high acceptance of the project.
3.5 Open Source Development Research
3.5.1 Open Source Development
| Development of Open Source Communities |
|---|
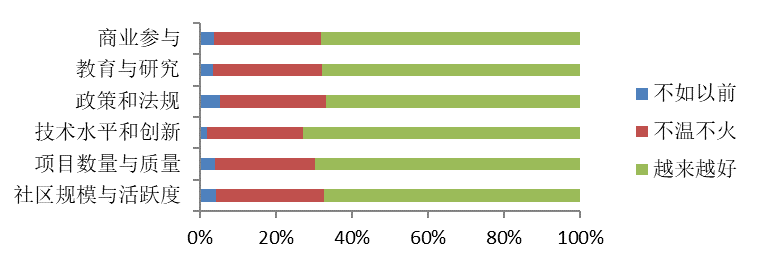 |
Overall, the respondents generally view the future development of open sources in the country as positive in all its aspects.
| Characteristics of the Continuous Development of Open Source Projects | Evaluation Indicators of Open Source Projects |
|---|---|
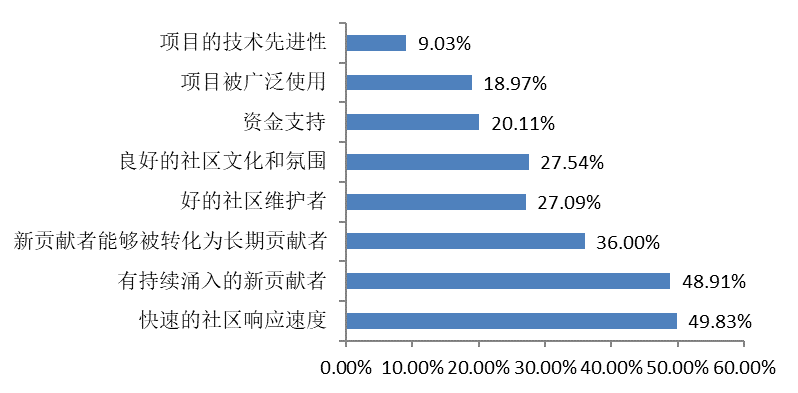 |  |
The respondents believe that the most important characteristic that affects the health and sustainability of an open source community is the speed of a rapid community response, and that new and emerging contributors with a continuing influx can be transformed into long-term contributors. Demonstrating long-term sustainability is critical to successful community development.
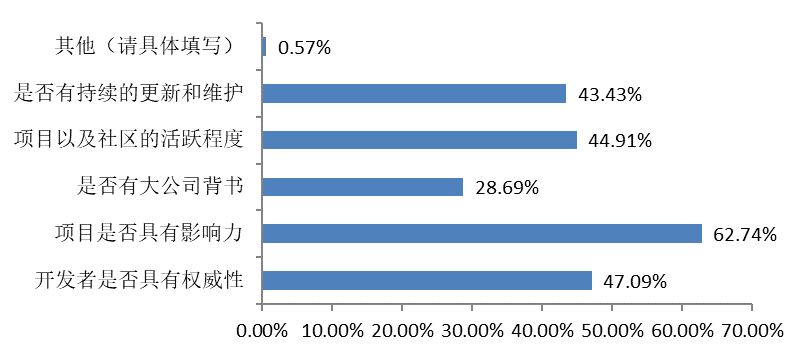
When evaluating open source projects, respondents mainly focus on project influence, authority, community activity and continued renewal and maintenance. This reflects developers' concerns about the overall state of health of the project at the technical and community levels.
3.5.2 Impact and Challenges of Artificial Intelligence on Developers and Open Source Ecosystem
| AI Impact on Developers | AI Future Role in Open Source Communities |
|---|---|
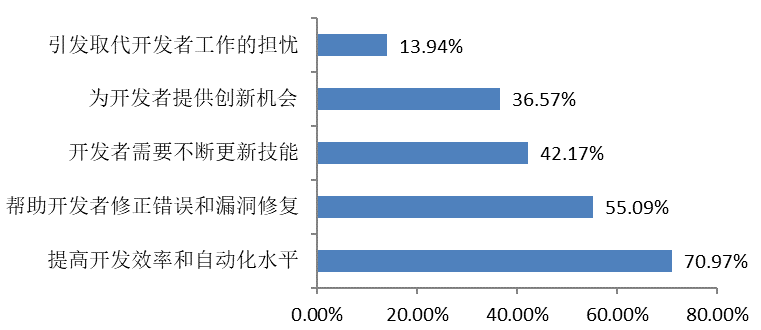 | 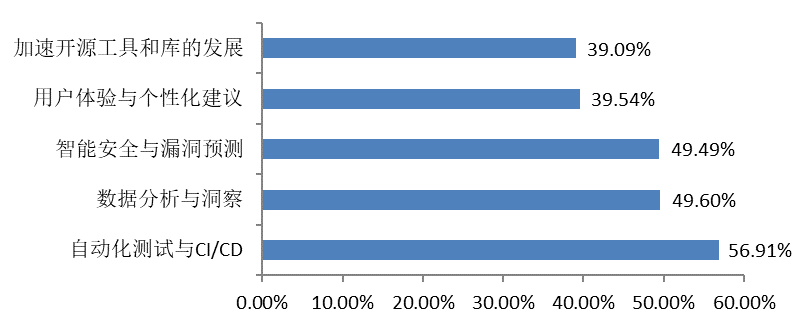 |
The survey results show that developers are more optimistic about the impact of artificial intelligence technologies on open source projects, especially in terms of greater application prospects for efficiency, automated testing, data analysis and project safety.
| Challenges for Artificial Intelligence in Open Source Ecosystem |
|---|
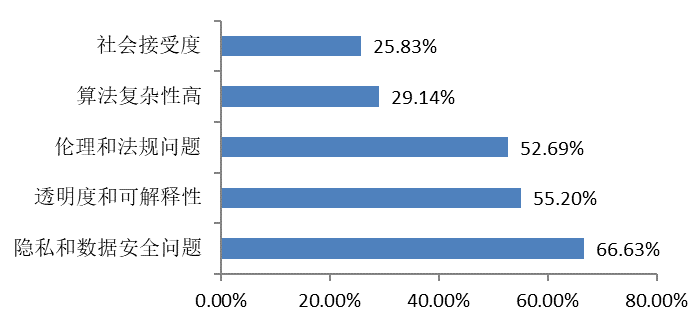 |
In addition, issues of privacy and data security, transparency and ethics are seen as major challenges facing artificial intelligence technologies in open source ecosystem, indicating the need to balance technological challenges and social considerations in AI technology applications.
:::Expert Commentary Jie YU:Faced with the wave of AI, we should remain calm and confident, embrace it with positive attitude, learning from it, and make full use of AI technology to promote the continuous development of individuals and projects. :::
 2023 COSR
2023 COSR